Hyper Text Transfer Protocol is the only protocol used for the communication between the client and the server. HTTP is a specification, majorly it is divided into two parts, they are:
- HTTP Request Format
- HTTP Response Format
HTTP Request Format:
This is the format used by the client to send request to the server. Majorly the client software(Browser) sends the request to the server in the following scenarios:
- When we type the URL and click on Enter.
- When we click on any button in the web page.
- When we click on the hyperlinks.
This HTTP Request Format is divided into four parts. The following figure shows the HTTP Request Format.
 |
| Fig1: HTTP Request Format |
Initial Request Line:
This line contains the Method name , Resource name and the Protocol/version. The following figure shows the Initial Request Line.
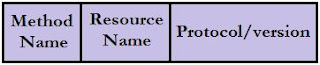 |
| Fig2: Initial Request Line block diagram |
There are so many methods available in JEE api. They are as follows:- GET
- POST
- PUT
- DELETE
- TRACE
- LOCATE
- HEAD
The default method that the client software(Browser) uses to communicate with server is GET.- Resource Name is the file name, which we want to be executed by the server.
- Protocol / version field gives the information about the protocol that is being used by the client to communicate with server.
The original Initial Request is as follows: 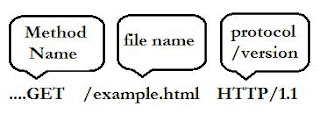 |
| Fig3: Original initial request line |
Zero or More no.of Headers:
The header is used to send extra information to the server. The following is the header format. |
| Fig4: Header Format |
Among all the headers, there are two most important headers, they are:- User-Agent (Indicates which browser program has sent the request to server)
- Accept Language (Specifies which language is acceptable by the client, based on this server sends the response )
Blank Line:
This line is used just to specify the gap between the headers and the request body.Request Body:
This is the optional part of the Http Request Format. Let us discuss about this in Post() method.HTTP Response Format:
This is the format used by the server to send the Response to the client. This format is divided into four parts as follows: |
| Fig5: Http Response Format |
Initial Response Line:
This is again divided into three parts as follows: |
| Fig6: Initial Response Line |
Protocol/version: Indicates the protocol used by the server to send the response to the client.Status Code: Indicates the status code of the request send by the server. The following are the status codes given by HTTP. 100 to 199 - Information200 to 299 - Success300 to 399 - Redirect400 to 499 - Requested Resource not available.500 to 599 - Failed to execute the Request.- If the server want to send the information to client then it sends 1XX.
- If the server is able to successfully process the request, it returns a status code 2XX.
- When the client send the request to a server, and if that server want us to check in another server, the server sends a status code 3XX to the client.
- If the requested resource is not available in the server, server will give 4XX status code.
- If the resource is available and if the server was unable to process the request then it sends 5XX Status code.
Status Message: Every response sent by the server will have a Status Message.
Ex: 200 - Success
404 - Not Found
Zero or More number of Headers:
Among all the headers Content Type is the only header which play a major role:
- Server sends this header to client to specify which type of content is being sent. Based on this the client displays the output.
Blank Line:
This is same as in the Request format.Response Body:
The data that server wants to send to the client will be added to the Response Body. The client receives the response body, formats it according to the tags and display to the user.
As of now we came to know about the HTTP Request and HTTP Response Formats. Now let us discuss about the methods that are used by the server. Method indicates the operation that has to be carried by the server.
Get(): This method is used to send the HTTP request to server and handle it.
Post(): This method also used to send the HTTP request to server and handle it.
Differences between Get() and Post():
When ever the user enter some data in the browser and click on submit button, it is the responsibility of the client to send the data entered by the user to the server. Suppose let us consider a login page. when the user enters the username and password and clicks on SUBMIT button, client sends the username and password to the server.
In the above example if we use Get() method, then the username and password is appended to the URL and sent to the server. - Ex: http://example.html?uname=graduate&pwd=cse
If the browser displays the URL as above everyone is able to see the data entered by the user, and at the same time get() method limits the URL characters to 1024. These two are the dangerous limitations of GET(). To overcome these two disadvantages, we should use POST().
When we use post() method, the data entered by the user is appended to the Request Body of the HTTP Request Format, so that no one can see the data entered by the user.
Put(): This method is used to place the resource from client to server. Because of security reasons non of the server supports put().
Delete(): This method is used to delete a resource available in the server. Because of security reasons non of the server supports put().
Trace()/Locate(): These methods are used when client wants to find the resources in server. Because of security reasons non of the server supports put().
Head(): When the client wants to know some info about the server, then the client sends Head request to the server. Server process the request and sends the response by using status code 1XX. Statefull & Stateless Protocols:
Based on their behavior Protocols are divided into two parts, they are:
- Statefull Protocol
- Stateless Protocol
Statefull Protocol:
A statefull protocol is the one which remembers the entire conversation between server and the client. We require huge amount of memory for statefull protocols. Ex: FTP, SMTP, UDP, TCP/IP etc..,
Stateless Protocol:
A stateless protocol is the one which do not remember the conversation between the client and server. These type of protocols require less amount of memory.Ex: HTTP
HTTPS(Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secured):
When we use HTTP we will face lot of security related problems, i.e., anybody can observe the username and password sent from the client to server. To resolve this problem we use HTTPS protocol. This protocol uses encryption algorithms, to encrypt the data.
For example when we open any browser and, we type www.gmail.com in the address bar, and press enter. After a small amount of time we can see the url converting to https:/www.gmail.com.