In java there are two types of Statements. They are:- Sequential Statements (statements which are executed one by one.)
- Control Statements (Statements which are executed repeatedly and randomly)
When we come to control statements, these are again divided into 3. they are:- Conditional or Decision Making statements(if-then, if-then-else, switch)
- Looping Statements(for, while, do-while)
- Branching Statements(break, continue, return)
if..else statement:
This statement performs the task based on the condition. The statements present inside the curly braces {} represents a task. The following is the syntax of this statement. |
| fig: if-else statement |
switch statement:
This statement consists of a set of cases which we have to choose according to our requirement. This statement is mainly used in menu driven programs. The following figure shows the syntax:
 |
| fig: Switch statement |
break statement:
This statement is used to break the flow of execution. This is used in 3 places, they are:- used in switch statement to come out of it.
- used in loops to come out of it.
- used in nested blocks to go to the end of the block.
continue statement:
This statement is used to skip the iteration of loops. The following program shows the use of continue statement. 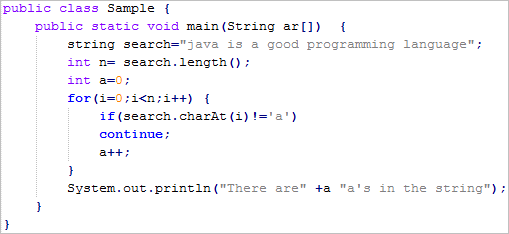 |
| fig: continue statement |
return statement:
Return statement is used to exit form the method. This statement has two forms, one which returns a value and one which doesn't. while loop:
The statements present in this loop executes continuously as long as the condition specified in the loop is true. The following is the syntax for while loop. |
| fig: while statement |
do...while loop:
The difference between while and do-while is that, In while loop, first the condition is checked and then the block of code is executed, where as in do-while first the block of code is executed and then the condition is evaluated. This means in do-while the block of statements are executed atleast once. The following is the syntax of do-while.
 |
| fig: doWhile statement |
for loop :
This loop iterates over a range of values, the following is the syntax of for loop. |
| fig: for loop |
for-each loop:
This loop is mainly used in collections. This loop repeatedly executes the statements for each element of a collection. The no.of iterations of this loop is equal to no.of elements in the collection. The following is the syntax.  |
| fig: for each loop |








This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete