- What is JVM?
JVM(Java Virtual Machine) is
a program whose responsible is to take the .class file and convert the byte
code instructions into machine code, and then make it executed by the
processor.
- What is a class loader?
Part
of JVM which loads the .class file into JVM's memory.
- Where does the memory is allocated to the class?
when
we run a java program class is stored in a runtime memory area called Method
Area.
These
are the functions that are copied form C,C++ header files.
- Why Java is a simple programming language?
It
contains no.of predefined functions, which makes a developer to fell free to
write the code.
- What are object oriented concepts?
The
concepts like class, object, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism are
object oriented concepts.
- What is a class?
Class
is an encapsulated body that consists of variables and methods.
- What is the difference between Method and Function?
Method/Functions
is described as a set of instructions that performs certain task. In Procedure
oriented language they are called as Functions, where as in Object oriented
language they are called as Methods.
- What is the difference between Public, Private and Protected?
Public, Private and Protected are the three access specifiers.
If we declare a class as public then the members of that class can be accessed
from any other classes. If we declare a class as private, then the members of
that class cannot be accessed by any other class. If we declare a class as
protected it can be accessed by only some classes.
- Which is the default package in java?
java.lang is the default package
in java.
- What is a static block?
The
block of code which is created with a static keyword, this block of code is
executed before the main() method execution.
eg: static{
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
}
- What are the different ways to accept input from keyboard?
There
are three different ways to accept input form keyboard:
using
BufferedReader
using
command line arguments and
- What is the error shows by the compiler if the main method is not available in program?
Exception in thread
"main" java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: main
- Does Java supports overriding?
No,
because overriding leads to confusion in JVM.
- Can we write a java program without using a class?
NO,
Since java is a pure Object oriented language we cannot write a java program
without class.
- What is an API?
An
API(Application Programming Interface) is a document that contains the
specifications that are to be followed while writing a program. It can be in
any format like .pdf, .html, .doc, .txt etc..,
- What is meant by a Garbage Collector? Can we invoke it manually?
Garbage
Collector is a program, that deletes the unused objects of a class. Yes, we can
invoke manually as "gc();".
- What is the difference between Assignment and Initialization?
The process of assigning the value to the variable is called
Assignment. We can assign a value to a variable any number of times. The
process of assigning the value to the variable at the time of declaration is called
as Initialization. Initialization can be done only once.
- What is the difference between equals() and "=="?
When
we compare two values using equals() it compares their values, but when we use
== it compares the hash values of the given values.
- What is the output of the following code?
System.out.println(1+2+"3");
System.out.println("1"+2+3);
Output: 33
123
- Which of the following is the most restricted access specifier?
protected
friend
static
Default
Protected
- What is the difference between a constructor and a method?
A constructor is a member function of a class that is used to
create objects of that class. It has the same name as the class itself, has no return type, and is
invoked using the new operator.
A method is an ordinary member function of a class. It has its
own name, a return type (which may be void), and is invoked using the dot
operator.
- What is the purpose of garbage collection in Java, and when is it used?
The purpose of garbage collection is to identify and discard
objects that are no longer needed by a program so that their resources can be reclaimed and
reused. A Java object is subject to garbage collection when it becomes
unreachable to the program in which it is used.
- What is the difference between StringBuffer and StringBuilder?
refer the following link
http://csegraduates.blogspot.in/2012/11/difference-between-string-and.html
- Which of the following is primarily accessed by the java compiler?(static block , static method, static variable.)
When we compile the program JVM first looks for the static
variables , then methods followed by blocks and allocates memory for them
respectively.
- What is the difference between Instance variables and Static variables(Class Variables)?
Instance Variables
|
Static Variables/Class Variables
|
A
separate copy is available to each object
|
Single copy in memory is shared by
all the objects
|
Instance
variables are created and stored in Heap Memory.
|
Static variables are stored in the
Method area.
|
- What is the difference between Instance Methods and Static Methods?
Instance methods are able to access both Instance variables as
well as Static variables, where as the Static methods are able to access only
Static variables.
- Why Instance variables are not accessed by the static methods?
JVM
creates the objects after the execution of Static methods. So, instance
variables of the objects are not accessed by the static methods.
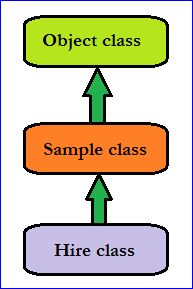
- What is inheritance?
Deriving
subclass from the super class is called as Inheritance.
- Why Java does not support Multiple inheritance?
Multiple
inheritance in java leads to confusion in programmer. Since Java is known for
simplicity, multiple inheritance is omitted in Java.
- How can we gain multiple inheritance in Java?
We
can gain multiple inheritance by using interfaces. i.e, by extending a class
and by implementing the interface.
- Can we create the super class object in the subclass?
Yes,
we can create the super class object in the subclass.
- What is polymorphism?
Polymorphism
means, a single object exhibiting different properties.
- What is meant by an abstract class?
An
abstract class is the class which consists of both abstract methods and
concrete methods.
- What is the difference between Interface and Abstract class?
Interface
is the one which consists of only abstract methods, where as the abstract class
consists of both abstract methods as well as concrete methods.
- Can we create the object to the abstract class?
No,
we cannot create the object to the abstract class.
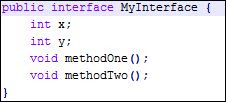
- What is meant by Interface?
Interface
is typical class which consists of only abstract methods, the class
implementing that interface should define all the methods in that interface.
- What is meant by type casting?
The process of converting one datatype into another is called as
Typecasting.